Industrial properties
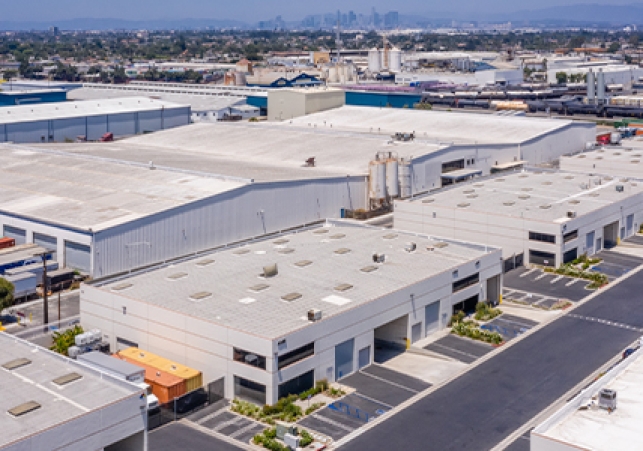

Industrial properties encompass a broad spectrum of real estate assets dedicated to manufacturing, distribution, storage, and research facilities. These properties serve as the backbone of various industries, providing essential infrastructure for production, logistics, and innovation. From sprawling warehouses to specialized manufacturing plants, industrial properties play a pivotal role in supporting economic activity and facilitating global trade.
Types of Industrial Properties:
-
Warehouses: Warehouses are perhaps the most common type of industrial property. They serve as storage facilities for goods awaiting distribution or manufacturing processes. Warehouses vary widely in size and design, ranging from small-scale storage units to massive fulfillment centers equipped with advanced automation technologies.
-
Manufacturing Plants: Manufacturing plants are specialized industrial properties designed for the production of goods. These facilities house machinery, assembly lines, and other equipment necessary for manufacturing processes. They often require large floor areas, high ceilings, and robust utility infrastructure to accommodate heavy machinery and ensure efficient production workflows.
-
Distribution Centers: Distribution centers are key nodes in supply chain networks, serving as hubs for the storage and distribution of goods. These facilities are strategically located to optimize transportation routes and minimize delivery times. Distribution centers often feature advanced logistics technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems, to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
-
Flex Spaces: Flex spaces are versatile industrial properties that can accommodate various uses, including office space, warehousing, and light manufacturing. These properties offer flexibility for tenants seeking adaptable spaces that can accommodate evolving business needs. Flex spaces are particularly suitable for small to medium-sized businesses operating in dynamic industries.
-
Research and Development (R&D) Facilities: R&D facilities are specialized industrial properties dedicated to scientific research, product development, and innovation. These facilities are equipped with laboratories, testing facilities, and collaborative workspaces to support research activities across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and advanced manufacturing.
Key Considerations in Industrial Property Investment:
-
Location: Location is a critical factor in industrial property investment. Proximity to transportation infrastructure, including highways, railways, and ports, is essential for facilitating efficient logistics operations and minimizing transportation costs. Additionally, proximity to major population centers and consumer markets can enhance the attractiveness of industrial properties for tenants and investors alike.
-
Property Characteristics: The physical attributes of industrial properties, such as building size, ceiling height, floor load capacity, and utility infrastructure, play a significant role in determining their suitability for specific industrial activities. Investors should assess these characteristics carefully to ensure that the property aligns with the needs of potential tenants or end-users.
-
Market Demand: Understanding market demand dynamics is crucial for assessing the investment potential of industrial properties. Factors such as vacancy rates, rental rates, absorption rates, and demand drivers (e.g., e-commerce growth, manufacturing expansion) can influence the performance of industrial real estate markets. Investors should conduct thorough market research to identify opportunities and mitigate risks.
-
Tenant Quality and Lease Terms: The creditworthiness of tenants and the terms of lease agreements are important considerations for industrial property investors. Long-term leases with reputable tenants can provide stable cash flows and reduce vacancy risks. Additionally, lease structures, such as triple net leases or gross leases, can impact the distribution of operating expenses and responsibilities between landlords and tenants.
-
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations: Industrial properties are subject to various regulatory requirements and environmental considerations, including zoning regulations, building codes, environmental permits, and remediation obligations. Investors should conduct due diligence to assess compliance with applicable regulations and identify any potential environmental liabilities associated with the property.
Trends Shaping the Industrial Real Estate Sector:
-
E-commerce Growth: The rapid expansion of e-commerce has driven demand for industrial properties, particularly distribution centers and fulfillment centers, to support last-mile delivery and same-day shipping services. As consumers increasingly turn to online shopping, industrial real estate markets have experienced heightened demand for modern logistics facilities located near major population centers.
-
Supply Chain Resilience: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience and accelerated trends toward inventory diversification and reshoring of manufacturing operations. Industrial properties located in close proximity to consumer markets have become increasingly valuable as companies seek to minimize supply chain disruptions and reduce reliance on overseas production.
-
Technological Innovation: Technological advancements, such as automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence, are reshaping the industrial real estate landscape. Modern warehouses and manufacturing facilities are incorporating advanced technologies to improve operational efficiency, enhance inventory management, and optimize supply chain logistics. Investors are increasingly focused on properties equipped with state-of-the-art infrastructure to capitalize on these emerging trends.
-
Sustainability and Green Initiatives: There is growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility within the industrial real estate sector. Developers and investors are incorporating sustainable design principles, energy-efficient technologies, and renewable energy sources into new industrial developments to minimize carbon footprints and reduce operating costs. Green certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), are becoming increasingly sought after by tenants and investors alike.
-
Adaptive Reuse and Redevelopment: With changing market dynamics and urbanization trends, there is a growing interest in adaptive reuse and redevelopment of existing industrial properties. Obsolete warehouses and manufacturing facilities are being repurposed for alternative uses, such as mixed-use developments, creative office spaces, or experiential retail destinations. These adaptive reuse projects offer opportunities to revitalize underutilized assets and unlock new value in urban areas.
In conclusion, industrial properties play a vital role in supporting economic activity, facilitating global trade, and driving innovation across various industries. Investors seeking to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the industrial real estate sector should carefully evaluate factors such as location, property characteristics, market demand, tenant quality, and emerging trends. By staying abreast of market dynamics and embracing technological advancements, investors can position themselves to succeed in this dynamic and evolving asset class.